Catheter Ablation in Patients with Electrical Storm. The Calm after the Tempest
pp. 543-546
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.7775/rac.v83.i6.6120Abstract
Background: Catheter ablation (CA) has been shown to be effective in patients with recurrent ventricular tachycardia (VT); however, its role in patients with electrical storm (ES) has not been studied in randomized trials.
Objective: The aim of this study was to analyze ES cases treated with CA.
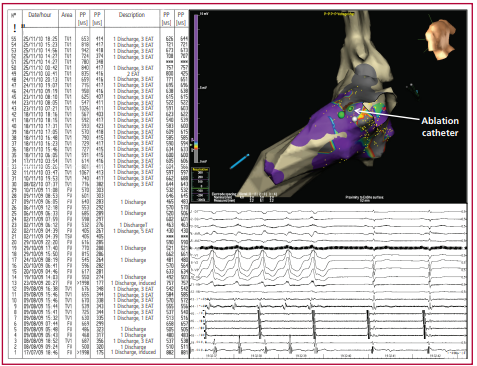
Methods: This was a retrospective analysis of patients treated with CA for ES due to sustained monomorphic VT (SMVT). Procedure success was defined as lack of inducible VT at the end of ablation, partial success as the induction of non-clinical VT, and failure as inducible clinical VT.
Results: Sixteen procedures were performed in 14 patients: 10 successful, 3 partially successful, and 3 failures. All patients were free from ventricular arrhythmia immediately after ablation. Ten patients (71.4%) were free from VT and 86.7% free from ES [8 (3–30)-month follow-up]. Five patients (35.7%) died from causes unrelated to arrhythmia.
Conclusions: Catheter ablation is associated with acute suppression of VT in all patients with ES due to SMVT and with a recurrence-free outcome in most of them.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Argentine Journal of Cardiology

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.













